What is psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic disease where the immune system becomes overactive, causing skin cells to multiply rapidly. This leads to the formation of thick, scaly patches of skin, commonly found on the elbows, knees, and scalp. These patches are often itchy, creating significant discomfort, particularly in cold or humid climates such as Singapore.
Where is it found?
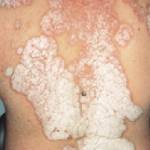
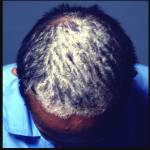
Affected areas can present as scaly patches on the scalp which are typically red and appear to be thicker and more extensive than regular dandruff. Nearly 50% of psoriasis cases have affected nails, and about 5-40% of individuals with extensive psoriasis experience severe joint pains and swelling.


How is psoriasis caused?
Psoriasis is usually caused by two factors: genetics and environment. Many individuals with psoriasis have a family member or relative with a history of the condition. In such patients, environmental factors such as extreme cold and dry weather can trigger this condition. Other factors that contribute to flare-ups include emotional and physical stress. For some patients, infections like flu or a throat disease can also trigger psoriasis, in addition to ingesting certain drugs such as anti-hypertensives.
Psoriasis typically develops in two phases: The early onset of psoriasis begins in the early twenties while the late onset begins in the age of 50 onwards.
Is psoriasis contagious?
No, psoriasis is not contagious and cannot spread or be transmitted from one person to another. However, if left untreated, it can spread from one area of the body to another. Proper care and treatment from a dermatologist are essential to managing and preventing the condition from worsening.
Will I pass on psoriasis to my children?
Although psoriasis is a hereditary skin condition, only about 40% of affected individuals have a family member or distant relative with a history of psoriasis. This chronic disease is caused by other factors, and inherited genes don’t always express psoriasis without the environmental factors that trigger it.
Is psoriasis a rare skin disease?
Psoriasis is known to affect at least 1-2% of Singapore’s population.
What treatments are available for psoriasis?
There are various psoriasis treatments that can help manage the disease, ranging from topical solutions to fairly recent therapies, such as:
-
- Topical Creams and Scalp Solutions: For individuals experiencing a milder form of psoriasis, using psoriasis cream or psoriasis ointment prescribed by a dermatologist can provide significant relief. These may include topical steroids or non-steroidal treatments such as a vitamin D3 derivative. Such treatments can also be beneficial in managing scalp psoriasis.
- Phototherapy: Another common option for psoriasis therapy is phototherapy, which involves exposing the affected skin to ultraviolet (UV) light. Both UVB and UVA have proven to be effective in treating psoriasis skin when administered in gradually increasing doses over a few months. To achieve optimal results, treatment usually needs to be done two to three times a week.
- Oral Medications: For more severe psoriasis cases, dermatologists may prescribe oral medication. While these medications can help manage psoriasis, regular monitoring with blood tests is vital owing to potential side effects, especially on the liver and kidneys.
- Biologics: These are a recent variety of drugs suitable for individuals with extensive or aggressive forms of psoriasis. Usually administered as injections, they target specific parts of the immune system, such as IL-17, IL-23, or TNF alpha, that cause psoriasis. Prescription medication has proven to be an effective and safe psoriasis solution for many patients.

 Contact us for
Contact us for
 Contact us for
Contact us for