
#facialflushing #redface #centrofacial #rosaceatreatment #howtoavoidskinredness
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by facial redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels. It affects millions worldwide, impacting quality of life and self-esteem. This comprehensive guide explores rosacea’s subtypes, symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
What is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a complex condition involving:
- 1. Abnormal blood vessel function
- 2. Inflammation
- Skin barrier disruption
Subtypes of Rosacea
The American Academy of Dermatology recognizes four primary subtypes:
- Type 1: Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): Persistent redness and visible blood vessels
- Type 2: Papulopustular / Inflammatory Rosacea (PPR): Redness, acne-like lesions, and pus-filled bumps
- Phymatous Rosacea: Thickened skin, nodules, and enlargement of facial features, especially the nose
- Ocular Rosacea: Eye symptoms, including redness, tearing, and burning
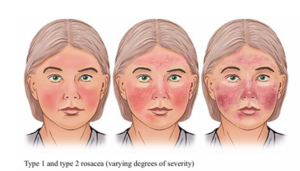
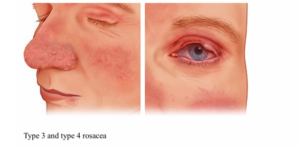
Credit: National Institutes of Health. (2023)
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Facial redness and flushing
- Visible blood vessels (telangiectasias)
- Acne-like lesions
- Swelling and inflammation
- Eye irritation
- Skin sensitivity
Caution: Signs and symptoms of rosacea can be often mistaken for eczema/ dermatitis or common acne.
Causes and Triggers
Factors contributing to rosacea:
- Genetics
- Hormonal changes
- Environmental factors (sun, wind, temperature)
- Skin care products
- Certain medications
- Food and drink (spicy, hot, or caffeinated)
- Stress
Treatment Options
A comprehensive treatment plan involves:
Topicals
- Metronidazole (antibacterial and anti-inflammatory)
- Ivermectin for inflammation and reduction of demodex mites (a type of skin organism that can contribute to skin irritation and inflammation)
- Brimonidine (vascular constriction)
- Azelaic acid (anti-inflammatory and antibacterial)
Oral Medications
- Antibiotics (doxycycline, minocycline)
- Isotretinoin (severe cases)
- Beta-blockers (for flushing)
Laser and Light Therapy
- Pulsed dye laser
- Intense pulsed light (IPL)
Lifestyle Modifications
- Sun protection (SPF 50+)
- Gentle skin care
- Avoid triggers (heat, spicy food) and managing stress
Surgical Options
- Rhinophyma (severe nasal enlargement) correction
- Electrosurgery or laser surgery for telangiectasias
Conclusion
Rosacea is a complex condition requiring personalized treatment. Understanding the subtypes, symptoms, and triggers enables effective management. A combination of topical treatments, oral medications, lifestyle modifications, and laser therapy can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)
- National Rosacea Society (NRS)
- Rosacea Support Group

 Contact us for
Contact us for
 Contact us for
Contact us for